Introduction
The Alveolus e.g, for example, is a crucial component of the respiratory system, playing a vital role in gas exchange. These tiny, balloon-shaped structures are located at the end of the bronchioles in the lungs. In this article, we will delve into the structure, function, and importance of the Alveolus e.g, and explore commonly associated disorders. By understanding the Alveolus e.g, for example, we can better appreciate its role in maintaining respiratory health.
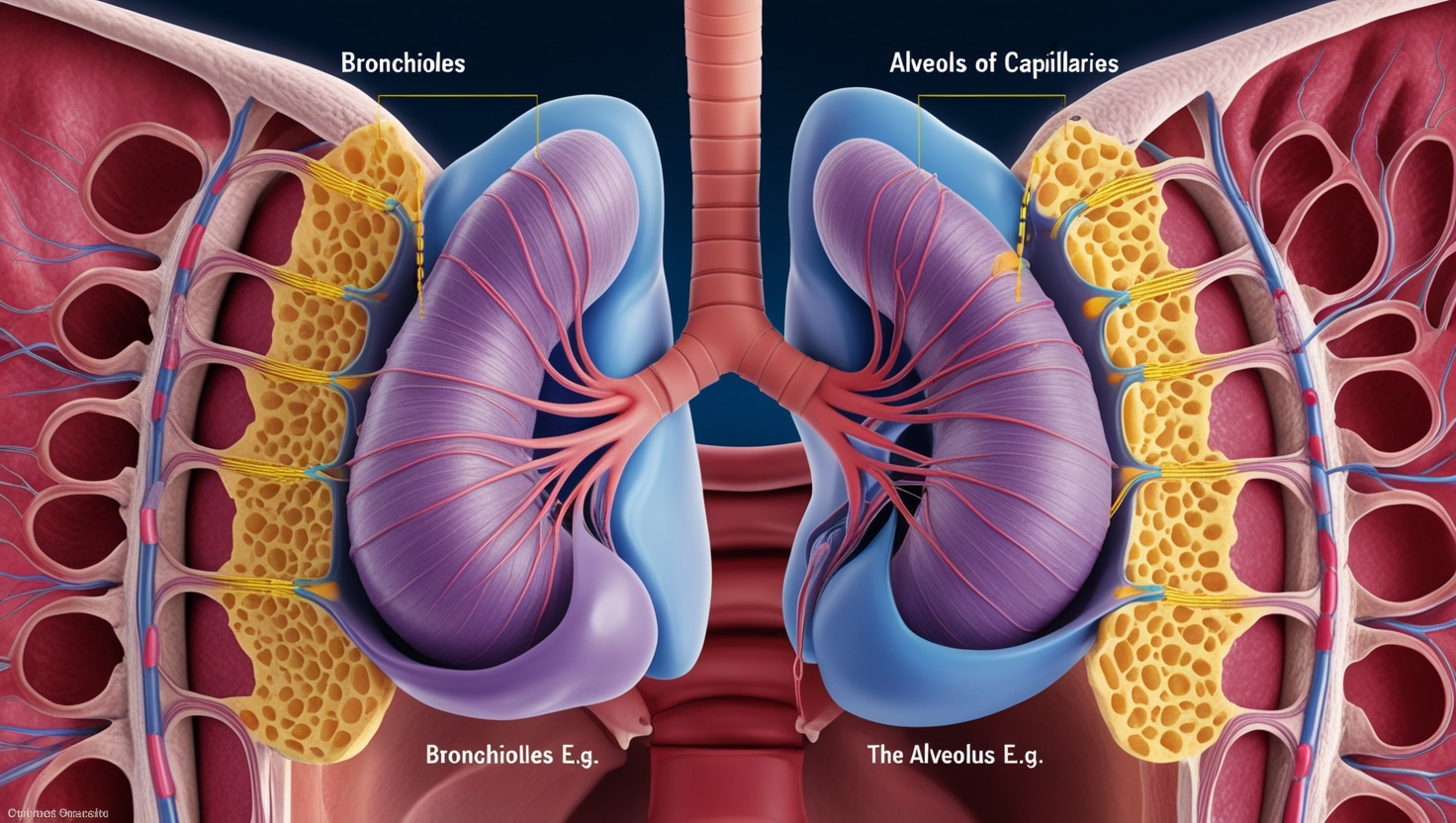
Structure of the Alveolus e.g
The Alveolus e.g, for example, is a small, thin-walled air sac typically arranged in clusters. Each Alveolus e.g is surrounded by a network of capillaries, which facilitate the exchange of gases. The walls of the Alveolus e.g, for example, are composed of a single layer of epithelial cells, allowing for efficient gas diffusion. This delicate structure is essential for the proper functioning of the respiratory system.
Function of the Alveolus e.g
The Alveolus’s primary function is to facilitate gas exchange between the air and the bloodstream.Oxygen from inhaled air diffuses through the alveolar walls into the capillaries, whereas carbon dioxide from the blood diffuses into the alveoli and is expelled. This procedure is essential for maintaining the body’s oxygen levels and eliminating waste.
Gas Exchange Process
The Alveolus e.g gas exchange process, e.g……., is driven by differences in partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Oxygen flows from higher concentrations in the alveoli to lower concentrations in the blood, whereas carbon dioxide goes in the reverse way. This efficient exchange is crucial for sustaining life and supporting cellular functions.
Role in Respiratory Health
The Alveolus e.g, for example, plays a significant role in respiratory health. Proper functioning of the alveoli ensures that the body receives adequate oxygen and expels carbon dioxide effectively. Any impairment in the function of the Alveolus e.g, for example, can lead to respiratory issues and affect overall health. Maintaining healthy alveoli is essential for optimal respiratory function.
Common Alveolar Disorders
Several disorders can affect the Alveolus, including pneumonia, emphysema, and pulmonary fibrosis. These conditions can impair gas exchange and lead to symptoms such as shortness of breath, coughing, and fatigue. Understanding these disorders and their impact on the alveolus is important for diagnosis and treatment.
Pneumonia and the Alveolus
Pneumonia is an illness that causes inflammation of the air sacs in one or both lungs. The alveolus, for example, fills with fluid or pus, making it harder for oxygen to enter the bloodstream. Bacteria, viruses, or fungi can cause this condition, requiring prompt medical attention to prevent complications.
Emphysema and Alveolar Damage
Emphysema is a chronic lung condition characterized by damage to the walls of the alveolus, e.g., which reduces the surface area available for gas exchange, leading to difficulty breathing and decreased blood oxygen levels. Smoking is a major risk factor for emphysema, highlighting the importance of lung health.
Pulmonary Fibrosis and Alveolar Scarring
Pulmonary fibrosis involves the thickening and scarring of the lung tissue, including the alveolus, e.g…….. This scarring can stiffen the lungs, making it harder for them to expand and contract. As a result, gas exchange becomes less efficient, leading to symptoms such as chronic cough and shortness of breath.
Impact of Smoking on Alveoli
Smoking harms the alveolus, e.g., causing inflammation and damage to the delicate structures. The harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke can lead to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and increase the risk of lung infections. Quitting smoking is crucial for protecting the health of the alveoli and overall respiratory function.
READ MORE: The Life and Legacy of G.G. Ginley: A Visionary Leader
Alveolar Regeneration and Healing
The alveolus, for example, has a limited capacity for regeneration and healing. While some damage can be repaired, extensive damage from chronic conditions or severe infections may be irreversible. Research is ongoing to explore potential therapies that can enhance alveolar regeneration and improve respiratory health.
Importance of Lung Health
Maintaining the health of the alveolus, for example, is essential for overall lung function. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and avoiding exposure to pollutants can help protect the alveoli. Additionally, early detection and treatment of respiratory conditions are vital for preserving alveolar function and preventing complications.
Advances in Alveolar Research
Recent advances in medical research have provided new insights into the function and disorders of the alveolus. For example, Innovative treatments and therapies are being developed to address alveolar damage and improve respiratory health. Continued research is essential for finding effective solutions for alveolar-related conditions.
Diagnostic Tools for Alveolar Disorders
Several diagnostic tools are available to assess the health of the alveolus. Imaging techniques such as chest X-rays and CT scans can reveal structural abnormalities. At the same time, pulmonary function tests measure gas exchange efficiency. These tools are crucial for diagnosing and monitoring alveolar disorders.
Treatment Options for Alveolar Conditions
Treatment for disorders affecting the alveolus, e.g., varies depending on the condition. Antibiotics may be prescribed for bacterial infections, while corticosteroids can reduce inflammation in conditions like pulmonary fibrosis. Oxygen therapy or surgical interventions may be necessary in severe cases to improve respiratory function.
Preventive Measures
For example, preventing damage to the alveolus involves adopting a healthy lifestyle and avoiding risk factors such as smoking and exposure to pollutants. Vaccinations can also protect against respiratory infections that can harm the alveoli. Regular check-ups and early intervention are key to maintaining alveolar health.
Role of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in diagnosing, treating, and managing conditions affecting the alveolus. For example, Pulmonologists, respiratory therapists, and primary care physicians work together to provide comprehensive care for patients with alveolar disorders. Their expertise is critical to improving patient outcomes.
Patient Education and Support
Educating patients about the importance of the alveolus, for example, and how to maintain respiratory health is vital. Support groups and educational resources can help patients manage their conditions and make informed decisions about their health. Empowering patients with knowledge is a key aspect of effective healthcare.
Future Directions in Alveolar Research
The future of alveolar research holds promise for new treatments and therapies. Advances in regenerative medicine, gene therapy, and personalized medicine have the potential to revolutionize the care of patients with alveolar disorders. Continued investment in research is essential for unlocking these possibilities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the alveolus, for example, is a fundamental component of the respiratory system, essential for efficient gas exchange and overall respiratory health. Understanding its structure, function, and the disorders that can affect it is crucial for maintaining lung health. By adopting preventive measures and seeking timely medical care, we can protect the alveolus and ensure optimal respiratory function. The ongoing research and advancements in medical science offer hope for improved treatments and better outcomes for patients with alveolar conditions.